Caterpillars Count! and the Macroecology of Bird Food

Our lab has developed a citizen science project called Caterpillars Count! which has beeen carried out at more than 200 nature centers, schools, and other sites throughout North America to better understand the phenology of foliage arthropods that birds rely on for raising young. We combine these data with other long term continental scale monitoring datasets of birds, butterflies, moths, and other insects to evaluate how climate change may be affecting the timing of spring leaf out, insect emergence, and bird migration. I am currently seeking a graduate student interested in working with the Caterpillars Count! dataset. Check out the Opportunities page.
- Arthropod community composition in urban landscapes is shaped by both environmental filtering and dispersal limitation
- Demographic consequences of phenological asynchrony for North American songbirds
- Phenology in adult and larval Lepidoptera from structured and unstructured surveys across eastern North America
- Spatiotemporal variation in avian migration phenology: citizen science reveals effects of climate change
- Caterpillars Count! A citizen science project for monitoring foliage arthropod abundance and phenology
- Migratory strategy drives species-level variation in sensitivity to green-up
Avian Richness and Community Structure

Birds are the group for which the most globally comprehensive data on distribution and diversity exist. In North America in particular, we have data on thousands of communities that in many cases span decades. Empirically, we find a strong positive relationship between measures of net primary productivity (or measures of climate that might reflect this) and species richness. One major aim of the lab is to more fully understand this macroecological relationship by conducting targeted field work collecting data on bird communities, but also on resource availability, habitat structure, and foraging behavior of key species over broad geographic gradients. In addition, we aim to incorporate data from other continental monitoring programs that include information on demography, population trends, and the phenology of migration and breeding. This research thus includes components of field work, sorting of arthropod (aka bird food) specimens, remote sensing, and modeling.
- Anthropogenic drivers of avian community turnover from local to regional scales
- The relative importance of biotic and abiotic determinants of temporal occupancy for avian species in North America
- Environmental filtering of avian communities along a rural-to-urban gradient in Greater Washington, D.C., USA
- Opposing mechanisms drive richness patterns of core and transient bird species
- Stochastic and deterministic drivers of spatial and temporal turnover in breeding bird communities
Macroecology
While the ideal gas laws are useless for describing the trajectory of any particular molecule they represent an extremely useful characterization of the behavior of molecules in general. Analogously, macroecology focuses on identifying general properties of populations, species, communities and ecosystems across the globe despite, or in some cases because of, the idiosyncratic differences among them. In particular, we are interested in ways to analyze large datasets that inform us about the ecological and evolutionary processes that structure assemblages. Examples of recent macroecological research in the lab include:
- Niche specialization in birds explains changes in range area, occupancy, and population size
- The prevalence and impact of transient species in ecological communities
- Aligning the measurement of microbial diversity with macroecological theory
- A new framework for inferring community assembly processes using phylogenetic information, relevant traits and environmental gradients
- Exploring the intersection of species-area and species-energy relationships.
- Utilizing information on phylogeny and functional traits to gain insight into community assembly processes.
Eco-Evolutionary Models of Diversification
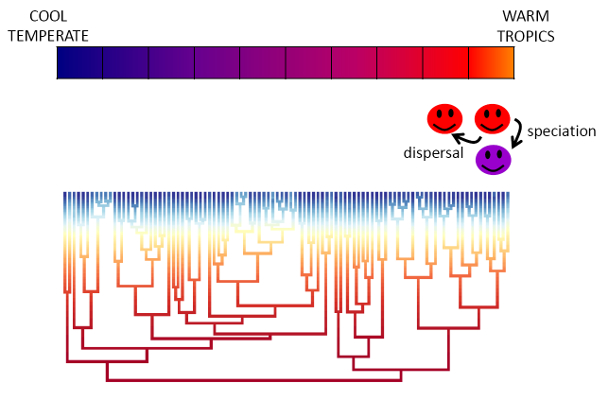
Observed patterns of distribution, diversity and turnover are the result of, to paraphrase G.E. Hutchinson, an evolutionary play unfolding within an ecological theater. We are interested in divining the processes and rules by which contemporary patterns have unfolded. One way of making such inferences is using in silico experiments in which we identify patterns in macroecological and phylogenetic structure of assemblages that seem to be diagnostic of particular processes involved in the diversification and dispersal of life across the globe. These simulation models can help us evaluate the myriad of biodiversity theories that have been put forward to explain pervasive patterns like the latitudinal gradient.
- A minimal model for the latitudinal diversity gradient suggests a dominant role for ecological limits
- When should species richness be limited and how would we know?
- On the processes generating latitudinal richness gradients: identifying diagnostic patterns and predictions
- The Latitudinal Diversity Gradient: Novel Understanding through Mechanistic Eco-evolutionary Models
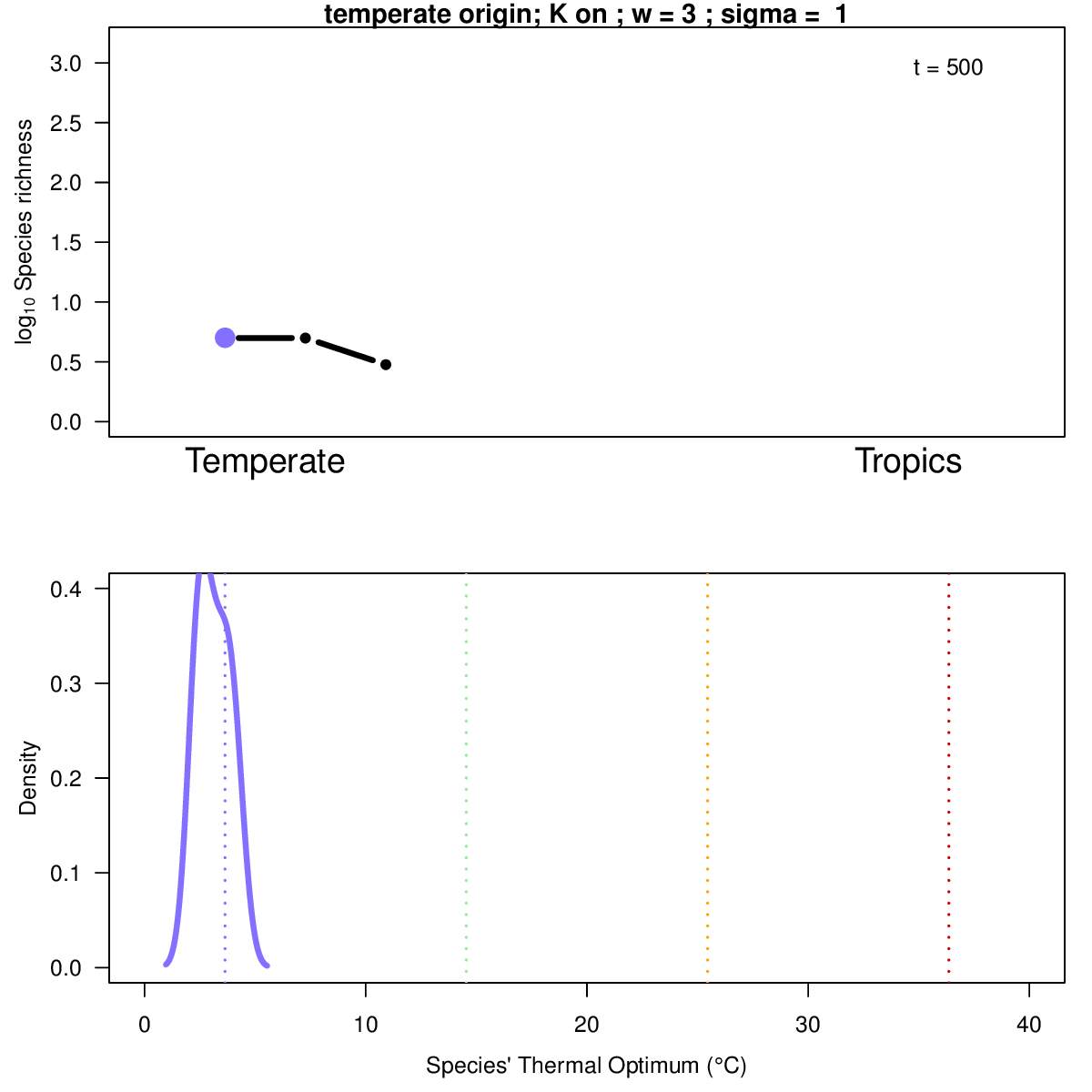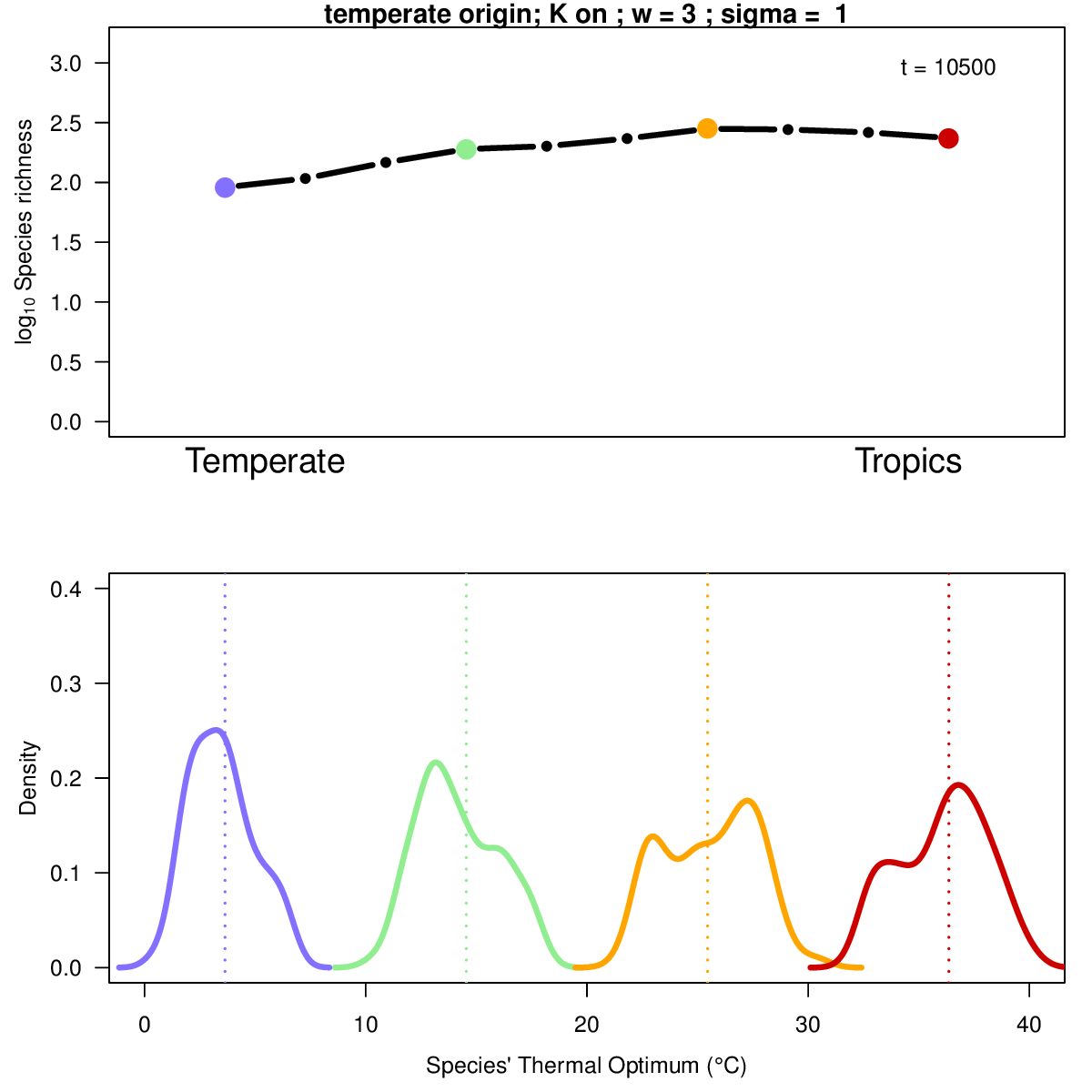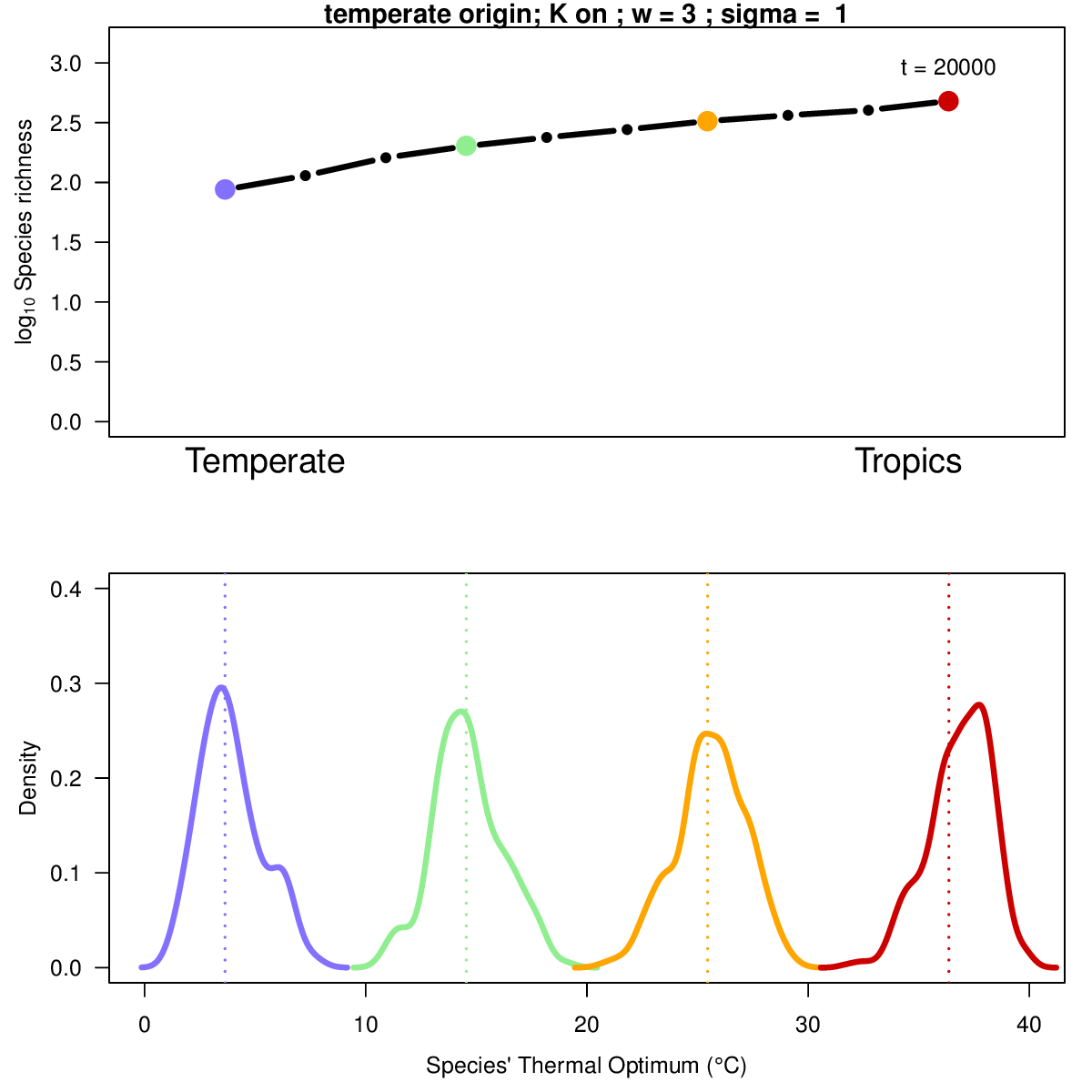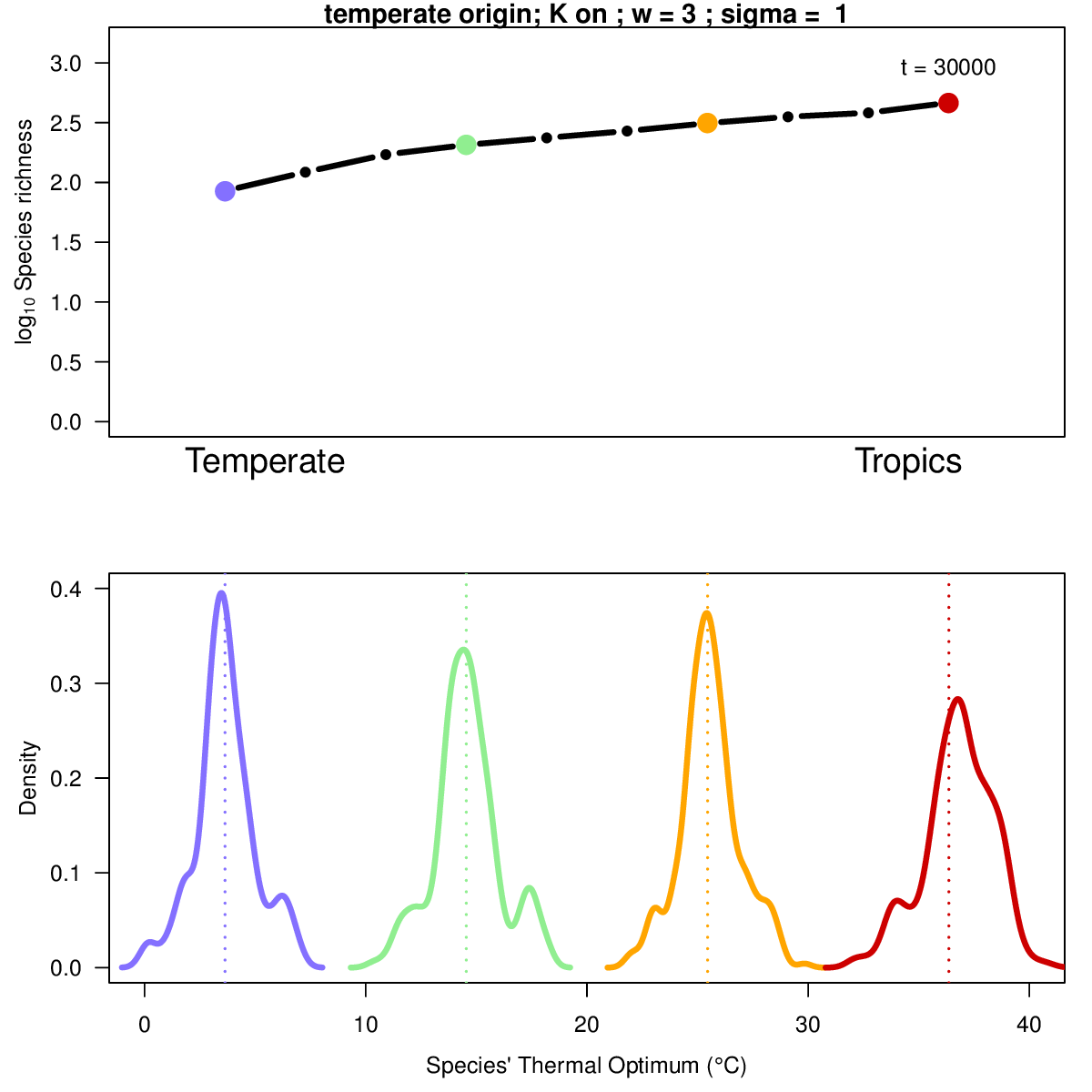
Animation illustrates the development of a richness gradient over time (top panel), and the distribution of species' thermal niches over time at four distinct locations (colors) across the spatial gradient (bottom panel). Click to enlarge.
Copyright © 2024 (Allen Hurlbert).