Embryology Biology 441 Spring 2010 Albert Harris
Mechanical forces and geometrical shapes
Some engineering and mathematical concepts embryologists need. (& 99% of biologists never learn about)

Stress = mechanical force per cross-sectional area: Either tensile stress or compressive stress
It has units of force per unit area .
Strain= proportional stretching or compression (produced by stresses)
What % has a material lengthened or shortened. (or sheared)
If all stresses were relieved, then how much would dimensions change
Young's modulus = the slope of the curve of stress per strain
Rubber has a small Young's modulus; Steel has a large one
Hooke's law = linear proportionality of stress to strain
If Young's modulus is constant, then a material is "Hookean"
But real materials are never Hookean beyond 1 or 2% strain.
Please understand that Hooke's law is NOT a law of nature.
It is a rule of thumb that is sometimes true.
At small strains (<1 or 2 %) it is true of many materials.
At large strains (>10% it is always more and more untrue)
Also, when Hooke's Law is not obeyed, then
Young's modulus is not constant, & so doesn't really exist
It's a proportionality constant for a ratio that isn't constant;
or the slope of a curved line (sometimes one with hysteresis!)
(hysteresis in the sense that the pull is stronger for a given % strain when you are applying force, but weaker as you release this stress)
SOME EQUATIONS WE WILL TALK ABOUT TODAY ARE EXACTLY TRUE.
Others are approximations. Hooke's Law is a useful approximation, but if the walls of your arteries obeyed this law (exactly) you would die of aneurisms!
The curvature of surfaces and layers may be the single most important variable for us to understand, in relation to shape.
Curvature = angular change of the tangent line per distance
(angular change per distance along a curve)




the Radius of Curvature = 1 / divided by curvature
(and has units of distance per radian of angular change)
(also, it is the radius of the circle that would most closely approximate a given section of a curve)
A straight line has zero curvature .
(and its radius of curvature is infinite, please notice)
A circle has constant curvature .
Curvature of small circles is larger than curvature of big circles.
A sphere has constant curvature in all directions .
A plane has zero curvature in all directions.
What is the curvature of the surface of a cylinder?
...of the surface of a cone?
...of the surface of a lemon?
...of the surface of an eyeball?, or a lens?
A cylinder has zero curvature in the lengthwise direction;
and has constant curvature in the circumferential direction.
Curvature of surfaces varies with direction,
for all shapes except for spheres or planes
(on which curvature is the same in all directions)
It turns out that stress and strain also can vary with direction.
And elastic moduli vary even more with direction.
(even if they happen to be constant in a given direction)
Differential Geometry is a division of higher mathematics in which shapes are defined in terms of curvatures, instead of the x, y. z coordinates that we learn about in elementary mathematics.


Stress, strain and curvature (of surfaces)
All 3 happen to be Tensor variables of the second order.
You know something about vectors , right?
You know vector variables have a direction as well as an amount;
in contrast to scalar variables, which have an amount at each place.
Examples of scalar variables: temperature, chemical concentrations
(also osmotic pressure, & water and gas pressures)
[assuming we can ignore wind or currents]
Examples of vector variables: wind speed, magnetic force
(also gradients of scalar variables are vectors)
Vectors can (correctly!) be regarded as tensors of the first order.
Scalar variables are regarded as tensors of zero order.
Stress, strain and curvature are tensors of the second order.
Elastic moduli are tensors of the fourth order.
(I think maybe birefringence is a tensor of the third order)
(and there are properties that are 5th, 6th etc. order tensors)

Do not be frightened by tensors. They are your friends.
A little knowledge of tensors is useful for intellectual self-defense.

A stretched string can exert sideways pressure
Tension * Curvature = sideways force P=T*C

"Tension " means the same thing as tensile stress.
Pressure across a flexible sheet of material obeys this equation:
Pressure = T * C + t * c
Because tension and curvature can vary with direction,
T & C the values in one direction,
t & c in the perpendicular direction
Really, it could be more accurate to take some kind of integral.
(there are better things to worry about than that, however)

For a soap film, the mechanism that generates the tension has the same strength in all directions: therefore: P = T * (C + c)
If we stretch a soap film across a curved ring, then P=0
so C = -c Which is another way of saying that, at each location on the film, curvatures in perpendicular directions are exactly equal & opposite
The pressure inside a big bubble
is smallerthan the pressure in a little bubble!!!
Inside any given bubble, Pressure is a constant at each part of the surface. Although stretching a bubble may cause this interior pressure to change, nevertheless P = T * (C + c)
so at each location, perpendicular curvatures vary inversely.
C+c = some constant
In a complex froth of bubbles, there will be different pressures in different bubbles, and curvatures will vary widely, but they will always obey these equations [EXACTLY]
The surface tension of bubble surfaces (and liquid interfaces) does not vary as a function of direction.
That is NOT true of a rubber sheet, or a balloon, or an eyeball, etc. much less of the surfaces of cells, or of epithelial sheets!
(liquid and bubble interfaces are special cases, not a law of nature)
When tension can vary with direction, then P = T*C + t*c
and so C and c don't vary inversely by such simple rules,
but the rules are still simple enough to be very useful.
This equation controls the shape of the eyeball:
P = constant (because it's a fluid gel inside)
T has a lower (weaker) amount in the cornea than elsewhere.
therefore curvature is larger in the cornea (i.e. it bulges out)
If T in the cornea is made 1/3 as strong as in the sclera, then the curvature of the cornea will be 3.00000 larger than the sclera.
You let me control the Ts and Ps: I can make the Cs do what I want!
Even just controlling Ts, and P being some constant, then the curvatures are almost completely at the mercy of the Ts.
Developmental biology is about how genes create & control anatomy
Much is about how curvatures are created by tensions (acto-myosin)
The equations above cause the shape of the brain, the shape of cartilages (and thereby, the whole skeleton), the shape of limb buds, the diameters and branching patterns of blood vessels, etc. etc. etc.
This is very important for plastic surgery, & many other specialties
To understand these issues even a little puts you way ahead.
Unfortunately, it is difficult to measure or map forces inside developing embryos, or to cause experimental changes in forces, or to predict exactly what differences are predicted by theories.
Much published research in this area has been based on fundamental mistakes, misunderstandings, and over-simplifications. (or worse)
For example, the directional elongation of cartilage is claimed to be caused by directional secretion of matrix and growth of cells.
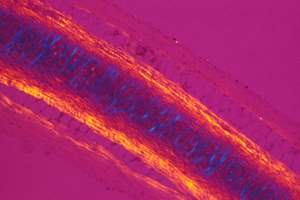

But the electro-osmotic pressure of cartilage is a scalar, which means it cannot possibly vary with direction. Pressure can vary from one location to another; and that can contribute to shape; but directional expansion has to be mostly caused by weakening of tension in one axis relative to tensions in the perpendicular axes.


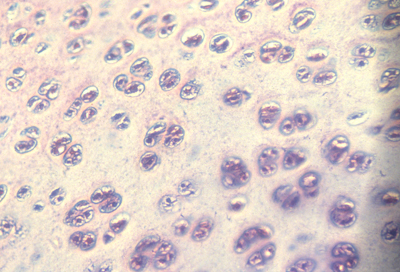

Reducing tensions inside embryos causes spatial irregularities and major birth defects, as extreme as doubling of organs.


These photographs show the development of the embryonic rudiments of feathers in pieces of bird skin. When the skin develops normally, on the embryos surface (or if it is kept under mechanical tension) then the feather rudiments form with highly-regular spatial periodicity. But when skin is clultured without the normal amount of mechanical tension, then the feather rudiments form at irregular positions.
On the surface of a soap film , or a balloon , in which the internal pressure is the same at all points on the surface, then pressure is equal to stress multiplied by curvature.
In other words, the local amounts of stress automatically adjust according to the local amounts of curvature , so that one multiplied times the other is a constant everywhere. To the extend that the material is flexible, & pressure is constant. If tension (=stress) becomes larger, then curvature becomes smaller.
Curves can be defined by the amount of curvature at each point. (Negative curvature means the line has curved back on itself)
Polarized light is one of the only methods by which one can "see" the complicated geometric patterns of mechanical stresses inside developing embryos.

Although the following is beyond the scope of this course, you may be interesting in knowing that one of the advantages of using mechanical forces for the direct control of anatomical patterns is that such mechanisms can directly optimize the geometrical arrangements of organs, for example in the branching patterns of blood vessels.



There is a classic problem in higher Mathematics called "Plateau's Problem" which is to calculate equations for the surface that has the minimum total area for a given perimeter. These diagrams show computer solutions for Plateau's Problem for an arbitrarily shaped edge. A soap film stretched across a wire will automatically "find" the shape that has the minumum total area. Any sheet of material that contracts with the same amount of tension in all directions will also "find" the shape with the minimum total area.
But if a sheet of material contracts with a stronger force in some directions than in other directions, then the shapes that it will form will be different than those formed by soap films. The shapes that are formed do not depend on whether the contracting layer is made out of soap, or rubber, or living cells. What matters is whether the tension varies with direction, or varies from place to place. If a layer of cells happens to contract with the same strength at each place, and in all directions, then the shapes it will form will be the same as would be formed by a soap film.
Unfortunately, when cell contraction happens to obey such simple rules, then many people say the force must be "surface tension". Our textbook does this several places. But active contraction by actin and myosin can obey simple rules, or it can obey more complicated rules, in the sense of exerting stronger stress at some locations than others, or stronger stress in some directions than others. Such increased asymmetry of the forces exerted is a very effective way to create anatomical shapes. Most embryologists have never learned the simplest concepts of tensor properties, or different kinds of symmetry. So when a contractile layer begins to contract more in one place that another, or more strongly in one direction than another, 99% of embryologists don't know how to think about what is happening.
You don't need to know it for this course, but the subfield of mathematics that finds shapes and equations that minimize or maximize some property is known as "The Calculus of Variations". So, Plateau's Problem is one of many problems that belongs to the calculus of variations.
Another name that you don't need to know for this course, but might be interested to know, is that of the category of computer simulations that predicts (simulates) shapes and tension patterns that will be produced by materials as a result of obeying a given set of rules. These are called "Finite Element Methods". Although the actual materials you are interested in consist of infinite numbers of points, the computer simulation is based on a deliberately simplified, and finite, set of points with forces acting between then.
Millions of dollars are spent on finite element simulations of anatomical organs, and more research of this kind is needed. For example, some finite element simulations of sea urchin gastrulation and of neurulation in birds and amphibians have been published in embryological journals.

Much further research is needed on this general topic. This research is being held back by mistaken theories that genes can only work by controlling the x, y, z coordinates where cells will differentiate. Sometimes, that's actually what happens (probably). But it's wrong to think chemical patterns always have to come first, and control mechanical and geometric patterns. But for people who have never heard of differential geometry or tensors, but only studied about x, y, z coordinates, tend to assume that coordinates are the only possible way genes could create geometrical patterns.